By Bern Grush
A self-locating, self-paying parking meter can dramatically improve workflow, enforcement and the political relationship between municipal parking management and its stakeholders. This technology meshes with existing pay-by-phone and pay-and-display systems.
Few parkers are likely to appreciate that municipal parking management is a considerably more complex matter than may appear when they are frustrated by no parking signs, parking citations, poles with multiple confusing instructions, loading zones, handicapped parking, no stopping, variable time limits, too little parking just where they want it, and so on. Municipal parking has many different requirements and there are many stakeholders with conflicting priorities involved in the task of fitting what is sometimes too many automobiles into the scarce spots along our urban streets. In any large urban area and many medium-sized ones, municipal parking management is certainly far more difficult than managing the lots or garages for suburban shopping malls.
Municipalities always want their parking spaces utilized correctly for traffic flow and safety reasons. They generally like to see a sensible occupancy level to ensure a balanced, vibrant commercial downtown—i.e., not so much that access is denied to some or that congestion is inadvertently encouraged. Nor so little that the commercial district might suffer and businesses relocate. Many cities need to generate sufficient revenue to fund the collection and enforcement process, and a significant number even seek to generate a surplus for their treasury.
Business associations want business traffic, including people that arrive in automobiles. This generally results in demand for plentiful free or cheap parking which cities can increasingly ill-afford from a financial or traffic management perspective.
Environmentalists consider the automobile and by association, parking, to be a problem—and they have a point. They may want parking to cost more, or to have less of it available. The logic of parking scarcity to discourage use…
In support of the Regional Growth Strategy policy to encourage reduced residential parking requirements in coordination with frequent transit service, Metro Vancouver conducted one of the most comprehensive studies of apartment parking supply and demand for a metropolitan area. Evidence was gathered from current and emerging trends, discussions with municipal planners and engineers, and developers, and the completion of two regional surveys. From this investigation, key findings and opportunities have been identified for consideration by municipalities and the development industry to achieve a better match between apartment parking supply and demand close to frequent transit.
Executive Summary
Encouraging compact communities, sustainable transportation choices, and housing affordability are well-established objectives in Metro Vancouver’s Regional Growth Strategy and Regional Affordable Housing Strategy. Parking is at the nexus of these objectives. Given that apartments represent over one-half of new housing starts in the region today and will remain so over the next three decades as the population grows by one million people, having current and efficient parking requirements are critical to the achievement of a sustainable region and livable neighbourhoods.
In metropolitan Vancouver, the cost of constructing on-site structured parking can range from $20,000 to $45,000 per stall, plus maintenance costs. Ensuring the parking requirements match actual demand can help reduce unnecessary housing development costs.
The Metro Vancouver Apartment Parking Study is one of the most comprehensive examinations of apartment parking supply and demand conducted on a metropolitan area. Through the exploration of emerging trends, review of past studies, discussions with municipal planners, engineers, and developers, and completion of two regional surveys, a robust evidence base was established.
Current and Emerging Trends
The amount of parking required in new apartment developments should reflect current and emerging trends. Transit ridership continues to increase year after year, in part from improved transit service levels and the expansion of TransLink’s Frequent…
By Neša Matic and Dwight Deugo
The proliferation of mobile devices and our reliance on them for a multitude of our daily tasks and activities has had an impact on the way we use parking services.
Today, mobile parking services, which are relatively new in Canada, are bringing the benefits of improved convenience of mobile payment and mobility. However, they are also seen as the first steps towards the future of mobile parking, where social media, location-based services and machine-to-machine communications (M2M) play important roles.
While the market adoption of smartphones is shifting the mobile landscape towards high-end users with growing data plans, mobile parking systems aiming to capture wider audiences will continue to embrace the mobile “basics”: text messaging (SMS, short messaging service) and voice technologies (voice recognition). By taking this approach, they significantly expand their target market of prospects and customers, including non-data mobile users (pre-paid), and are able to cater to a wide variety of devices (iOS, Android, Windows).
In Ottawa, there are a few mobile parking payment systems already in operation. This article looks at one such system currently deployed at Carleton University and Algonquin College, through the eyes of two of its users and two of its vendor parking managers. The graphs below show the adoption rate of mobile parking payments at the Carleton University and Algonquin College.
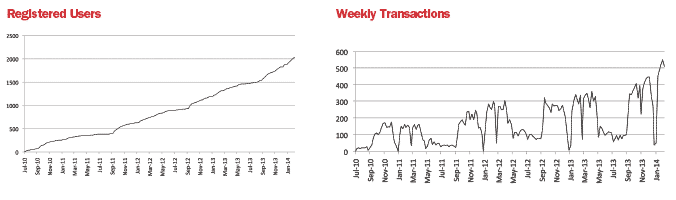
Emilie is a Carleton University student. She normally uses public transportation, but twice a week she drives her father’s car to school. Emilie’s father registered his credit card and Emilie’s mobile phone details with Carleton University’s mobile parking payment system so she can use her mobile phone when parking in one of the university’s lots.
Always in a hurry, Emilie is often late for class. She parks her car in the P1 parking lot…



